In the exciting realm of blockchain technology, Ethereum stands out as one of the most prominent and widely used platforms. A critical component of the Ethereum network is its nodes, which play a vital role in maintaining the network’s functionality, security, and decentralization. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Ethereum nodes, exploring their various types and the significant benefits they bring to the blockchain ecosystem.
Ethereum, often referred to as the “world computer,” has gained immense popularity due to its smart contract capabilities and decentralized applications. At the heart of the Ethereum network are nodes, which are essentially computers that participate in maintaining the blockchain’s integrity. These nodes work together to validate transactions, execute smart contracts, and ensure the network’s overall health.
What are Ethereum Nodes?
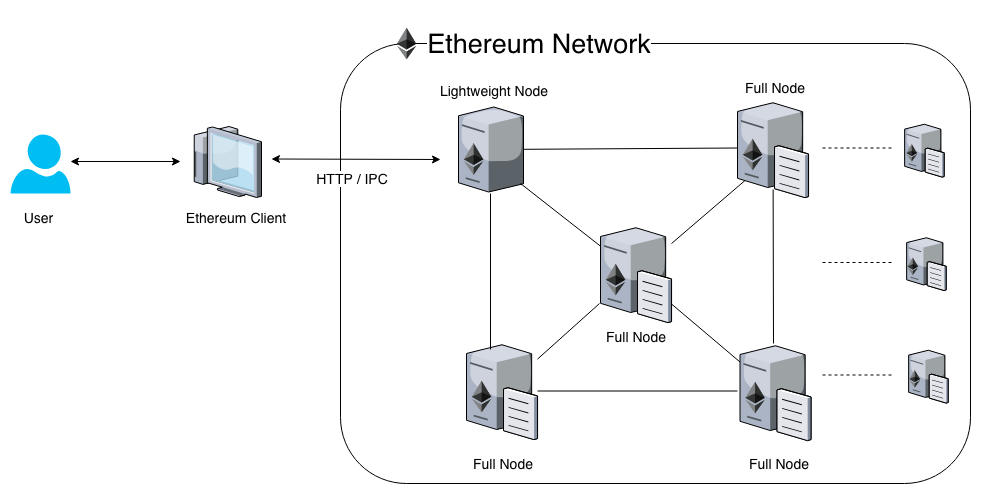
Ethereum nodes are individual computers or devices connected to the Ethereum network. They play a crucial role in maintaining a decentralized and secure ecosystem by validating transactions and blocks. Nodes communicate with each other to reach consensus on the state of the blockchain. There are several types of Ethereum nodes, each serving different purposes within the network.
Full Nodes
Full nodes are the backbone of the Ethereum network. They maintain a complete copy of the blockchain, including all historical data and smart contracts. Full nodes validate transactions independently and do not rely on third parties. This redundancy contributes to the network’s security and decentralization.
Features and Functions
Full nodes store the entire transaction history of the Ethereum blockchain. They validate transactions and blocks by checking the cryptographic signatures and ensuring that the transactions follow the network’s rules. Full nodes are also capable of broadcasting transactions to other nodes, contributing to the propagation of data across the network.
Importance in Network Security
The presence of numerous full nodes enhances the security of the Ethereum network. If one node becomes compromised or malicious, other nodes can cross-verify the information, preventing fraudulent transactions from being included in the blockchain. This decentralized validation process makes the network resilient against attacks.
Archive Nodes
Archive nodes go beyond full nodes in terms of data storage. They store all historical data, including past states of the blockchain. Researchers, analysts, and developers often rely on archive nodes to explore historical transactions and study the evolution of the network over time.
Storing Historical Data
Archive nodes enable the retrieval of any data from any point in the past, making them invaluable for in-depth analysis and research. They facilitate the examination of past smart contract states, transaction details, and account balances, aiding developers in debugging and optimizing their applications.
Research and Analysis
Researchers can use archive nodes to gain insights into network trends, usage patterns, and transaction history. These nodes are instrumental in understanding the dynamics of the Ethereum ecosystem and making informed decisions for its future development.
Light Nodes
Light nodes offer a more resource-efficient way to interact with the Ethereum network. Unlike full nodes and archive nodes, light nodes do not store the entire blockchain history. Instead, they rely on other nodes to provide them with specific data when needed.
Reduced Resource Requirements
Light nodes are suitable for users with limited storage capacity or processing power. They can quickly sync with the network and verify transactions using fewer resources. This convenience comes at a trade-off, as light nodes sacrifice some level of security and decentralization due to their reliance on other nodes for data.
Benefits of Running an Ethereum Node
Running an Ethereum node comes with several benefits that contribute to the overall health and resilience of the network.
Ensuring Network Reliability
By operating a full node, you actively participate in the network’s validation process. This helps in maintaining an accurate and up-to-date blockchain ledger, ensuring the reliability of transactions and data.
Data Access and Verification
Ethereum nodes provide easy access to blockchain data, allowing users to verify transactions and smart contracts independently. This transparency enhances trust and accountability within the ecosystem.
Contributing to Decentralization
Running a node contributes to the decentralization of the Ethereum network. The more nodes there are, the more distributed and secure the network becomes, as it becomes increasingly difficult for any single entity to control the majority of the nodes.
Setting Up Your Own Ethereum Node
Setting up an Ethereum node requires careful consideration of hardware and software requirements.
Hardware and Software Requirements
Running a full node typically demands a computer with sufficient storage and processing power. The Ethereum software, such as Geth or Parity, needs to be installed and configured to sync with the network.
Syncing with the Network
Syncing a node involves downloading the entire blockchain history and keeping it up-to-date. This process can take time and requires a stable internet connection. Once synced, the node actively participates in the network’s consensus mechanism.
Challenges and Considerations
While running an Ethereum node offers many advantages, there are also challenges to consider.
Resource Intensity
Operating a full or archive node can be resource-intensive due to the storage and processing requirements. Users should assess their hardware capabilities before committing to running a node.
Technical Expertise
Setting up and maintaining a node requires technical knowledge. Users need to understand how the Ethereum software works, as well as how to troubleshoot potential issues that may arise.



Leave a Reply